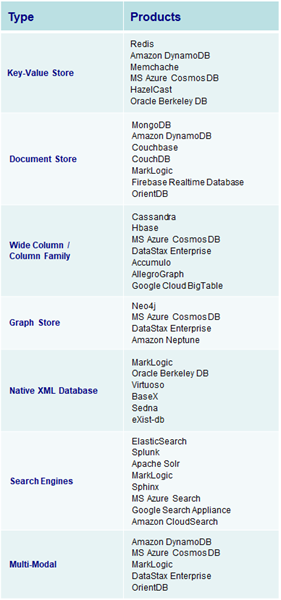
Search Engine NoSQL Database
Search Engine NoSQL Database
 Search engine databases are NoSQL databases that deal with data that does not necessarily conform to the rigid structural requirements of relation database management systems (RDBMS) as data for search may be text-based, semi-structured, or unstructured. Search engine databases are made to help users quickly find information they need in a high-quality and cost-effective manner. They are optimized for key word queries and typically offer specialized methods such as full-text search, complex search expressions, and ranking of search results.
Search engine databases are NoSQL databases that deal with data that does not necessarily conform to the rigid structural requirements of relation database management systems (RDBMS) as data for search may be text-based, semi-structured, or unstructured. Search engine databases are made to help users quickly find information they need in a high-quality and cost-effective manner. They are optimized for key word queries and typically offer specialized methods such as full-text search, complex search expressions, and ranking of search results.
Search engine databases contain two main components. First content is added to the search engine database index. Then when a user executes a query, relevant results are rapidly returned utilizing the search engine database index. Fast search responses are possible because instead of searching the text directly, queries perform searches against an index. This is the equivalent of retrieving pages in a book related to a keyword by searching the index at the back of a book, as opposed to searching each of the words in each page of the book. This type of index is known as an inverted index, because it converts a page-centric data structure to a keyword-centric data structure.
Search engine databases commonly support the following types of search functionality:
• Full-text search: Compares every word of the search request against every word within a file. Examines all the words in every stored file that contains natural language text such as English, French, or Spanish. And is appropriate when data to be discovered is mostly free-form text like that of a news article, academic paper, essay, or book.
• Semi-structured search: Searches of data that have both the rigid structure of an RDBMS and full-text sentences like those in a MS Word or PDF document as they can be converted to either XML or JSON format. Semi-structured data is a form of data that has a self-describing structure and contains tags or other markers to separate semantic elements and enforce hierarchies of records and fields within the data.
• Geographic search: Associates locations to web resources in order to answer location-based queries. Search results will not only be related to the topic of a query, but they will also be related to a physical location associated with the query. Thus, physical locations will be retrieved are in proximity of the search topic.
• Network search: Offers a relationship-oriented approach to search that lets users explore the connections in data within stored documents. This can include linkages between people, places, preferences, & products and is useful in discovering relevance of relationships. The search engine processes natural language queries to return information from across network graphs
• Navigational search: Augments other search capabilities with a guided-navigation system allowing users to narrow down search results by applying multiple filters based on classification of items. Navigational search uses a hierarchy structure or taxonomy of categories to enable users to browse information by choosing from a pre-determined set of categories. This allows a user to type in a simple query, then refine their search options by either navigating or drilling down into a category.
• Vector search: Ranks document results based upon how close they are to search keywords utilizing multi-dimensional vector distance models. Vector search is a way to conduct “fuzzy search”, i.e. a way to find documents that are close to a keyword. They help find inexact matches to documents that are “in-the-neighborhood” of search keywords.


 Recently,
Recently,