Overview of Data Lake Concept
Overview of Data Lake Concept
Data Lakes are storage repositories that hold a vast amount of raw data stored in the data’s native format. Types of data included in a data lake include structured data, relational databases, semi-structured data, unstructured data, documents, binary files, & raw data. The concept of data lakes has been well received by organizations that need to capture and store raw data of many different types at scale and low cost to perform data processing. The implementation characteristics of a data lake, namely inexpensive storage and schema flexibility, make it ideal for big data analysis and data science. The data lake has become a viable solution because it provides a cost-effective and technologically feasible way to store and analyze big data.
Data Lakes include the capabilities to store data of any size, shape, and speed, and enable all types of processing and analytics across platforms and languages. Further, data lakes remove the complexities of ingesting and storing data while making it faster to get up and running with batch, streaming, and interactive analytics. In the past, data lakes have typically been built using Hadoop, and enterprise Hadoop distributions such as Hortonworks and MapR which offer data lake architectures. Now organizations can also build data lakes by using infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) clouds including Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure. Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) supports data lakes while Microsoft has a dedicated Azure Data Lake platform to store and analyze real-time data.
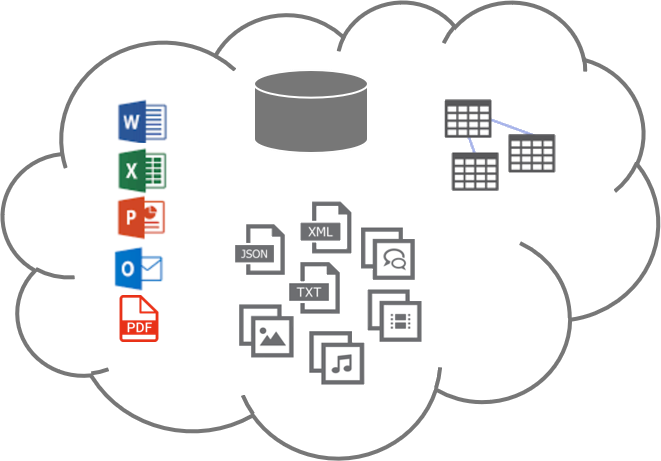
Data Lakes Can Include:
• Structured data from relational databases (rows and columns)
• Semi-structured data (CSV, Logs, XML, JSON)
• Unstructured data (Emails, Word, Excel, Powerpoint, Documents, PDFs)
• Binary data (graphics, images, audio, video)
Data Lakes are Characterized by Four Key Attributes:
1. Storage of All Data: Data lakes contain all types of data including structured, semi-structured, unstructured, and binary data formats.
2. Flexibility of Analysis: Data lakes enable users across multiple business units to explore and analyze data on their own terms.
3. Multiple Access Techniques: Data lakes enable multiple data access patterns including batch, interactive, online, search, in-memory, and other analysis engines.
4. Shared Infrastructure: Data lakes provide a single repository of data that is available to all data consumers within an organization.