Data Science – Discovering Information from Data
Data science is a broad field that refers to the collective processes, theories, concepts, tools and technologies that enable the ability to gain knowledge and insights from all forms of raw data. Further, data science combines different fields of work, techniques, and disciplines in order to interpret data for the purpose of decision making. It employs techniques and theories drawn from many fields within the context of mathematics, statistics, information science, and computer science. However, Data science is ultimately about analyzing data in creative, methodical, and sophisticated ways to generate business value.
Much like science is a generic term that includes a number of specialties and disciplines, data science is a broad term for a variety of techniques to discover information from sets of data. Included in data science are techniques of scientific method, mathematics, statistics, computer programming, machine learning, data analysis, and business analysis. If it is a technique performed on data to analyze it or discover information from data, it most likely falls within the field of data science.
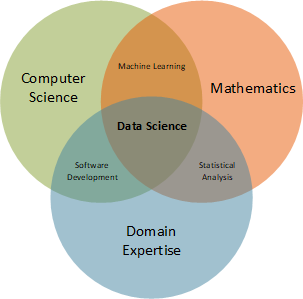
The most basic disciplines that make up the field of data science are computer science, mathematics, and domain expertise. And where the basic disciplines intersect, data science also includes cross-functional disciplines of machine learning, statistical analysis, and software development.
Each of the basic disciplines within data science are defined as:
• Computer Science: Encompasses both the theoretical study of algorithms (i.e. well-defined procedures that allows a computer to solve a problem), and the practical problems involved in implementing algorithms in terms of digital computer hardware and software.
• Mathematics: The study of the measurement, properties, and relationships of quantities and sets, using numbers and symbols including arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and calculus.
• Domain Expertise: Deep understanding and knowledge in a specific business area, business process, business area, business function, or technical subjects for a project or program.
Each of the cross-functional disciplines within data science are defined as:
• Machine Learning: An application of artificial intelligence that provides systems the ability to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
• Statistical Analysis: Science of collecting, exploring and presenting large amounts of data in order to discover probability, relationships, correlation, and trends.
• Software Development: Process of designing, programming, & deploying executable computer programs for the purpose of accomplishing a specific computing task.
With the use of many techniques and tools, data science can add value to any organization in any industry that would like to utilize their data to make better decisions. And the goal of data science is to construct the means for extracting business-focused insights from data. Fundamentally, data science utilizes a variety of sophisticated techniques and tools to conduct analysis on large and varied data sets for the purpose of generating useful information.