Balanced Scorecard Defined
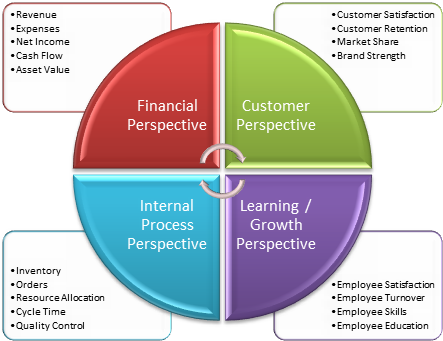
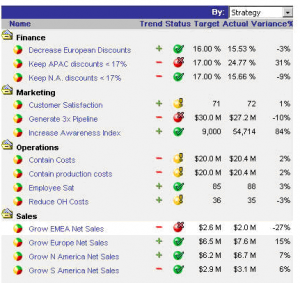
A Balanced Scorecard is a performance management tool used by executives and managers to manage the execution of organizational activities and to monitor the results of actions. Fundamentally a balanced scorecard provides a summary level view of organizational performance at a quick glance and includes key performance indicators (KPIs) across four main areas or perspectives:
Financial Perspective: KPIs for productivity, revenue, growth, usage, and overall shareholder value.
Customer Perspective: KPIs for customer acquisition, customer satisfaction rates, market share, and overall brand strength.
Internal Process Perspective: KPIs for resource usage, inventory turnover rates, order fulfillment, and quality control.
Learning / Growth Perspective: KPIs for employee retention, employee satisfaction, and employee education, training, and development.
The balanced scorecard concept was originated by Drs. Robert Kaplan (Harvard Business School) and David Norton as a framework for managing and measurement organizational performance. The concept added strategic non-financial performance measures to traditional financial metrics to provide executives and managers a more ‘balanced’ and ‘holistic’ view of organizational performance. Over time the balanced scorecard has evolved from its early use as a simple performance measurement tool to a complete strategic planning and management system. The latest version of the balanced scorecard transforms an organization’s strategic plan from a passive document into the active actions the organization needs to perform on a daily basis. Additionally, it provides a framework that not only provides performance measurements, but helps planners identify what should be performed and what should be measured.
Adapted from Microsoft Technet and Balanced Scorecard Institite.