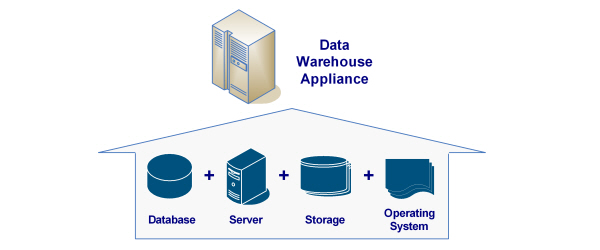
Basic Architecture of a Data Warehouse Appliance
By definition, a data warehouse appliance is a complete hardware and software solution that contains a fully integrated stack of processors, memory, storage, operating system, and database management software. The data warehouse appliance is typically constructed to be optimized for enterprise data warehouses, designed to handle massive amounts of data and queries, and designed to scale and grow over time. At its core, a data warehouse appliance simplifies the deployment, scaling, and management of the database and storage infrastructure as it provides a self-managing, self-tuning, plug-and-play database management system that can be scaled out in a modular manner.
- Fundamentally, a data warehouse appliance is a fully-integrated solution that contains …
- – Database Management System (DMBS)
- – Server Hardware
- – Storage Capabilities
- – Operating System (OS)
The primary factor for the platform scalability and large-query optimization of the data warehouse appliance is its massively parallel processing (MPP) architecture. These MPP architectures are comprised of numerous independent processors or servers that all execute in parallel. Also known as a “shared nothing architecture”, the MPP appliance architecture is characterized by a concept in which every embedded server is self-sufficient and controls its own memory and disk operations. Further, the MPP architecture effectively distributes data amongst a number of dedicated disk storage units connected to each server in the appliance. Computations are moved as close to the data as possible and data is logically distributed amongst numerous system nodes.
Almost all large operations in the data warehouse appliance environment, including data loads, query processes, backups, restorations, and indexing are executed completely in parallel. This divide-and-conquer approach allows for extreme high performance and allows for systems to scale linearly as new processors can easily be added into the environment.