Dimensional modeling is a specific discipline for modeling data that is an alternative to entity-relationship (E/R) modeling. A dimension model contains the same information as an E/R model but packages the data in symmetric format whose design goals are user understandability, query performance, and resilience to change.
Ralph Kimball, PhD, The Data Warehousing Lifecycle Toolkit, 1998
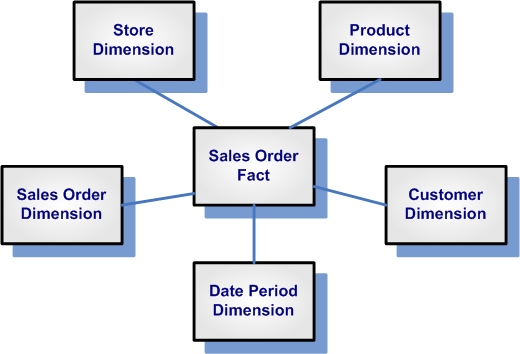
Basic Dimensional Model (Star Schema)
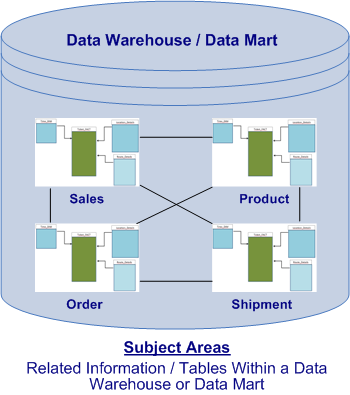
Dimensional modeling is a data modeling technique used to support on-line analytical processing (OLAP) systems and is implemented in databases that host either an enterprise data warehouses or data marts. The key point on the design of dimensional models is to resolve questions in the format “measures by dimensions.” In addition, dimensional models are commonly referred to as star schema as they comprised of a central fact table surrounded by several dimension tables.
- Within a dimensional model or star schema, there exists two types of data entities or tables …
- • Facts (Measurements – Numerical Values)
- • Dimensions (Contexts and Attributes – Text, Strings, Dates, & Flags)
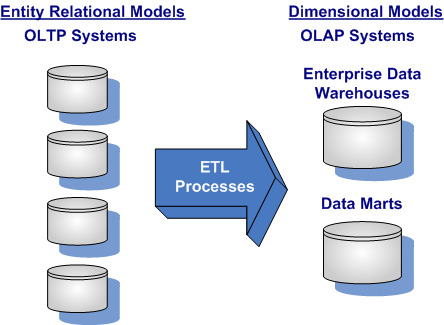
Transactional (OLTP) Systems to Analytical (OLAP) Systems
Within an enterprise data warehouse or data marts, data is fundamentally static, non-volatile and does not get updated. Rather data is inserted or loaded in bulk into the tables in the model utilizing using batch programs or extraction, transformation, & loading (ETL) routines. End-users of dimensional models develop queries that either read or select data, and there is no end-user inserting, updating, or deleting of data. Data in dimensional databases requires data to be converted or extracted from on-line transactional processing (OLTP) or other OLAP systems.
- The key benefits of dimensional models and data warehouses include ….
- • Separate environment from transactional systems
- • Allows for high-performance of select/read queries
- • Insulated from changes in source systems
- • Intuitive to developers and business users of queries
- • Contains data from multiple source systems
- • Optimized format for data warehouses and data marts