Data Lineage and Data Provenance
Data Lineage and Data Provenance commonly refer to the ways or the steps that a data set comes to its final state. Moreover, these two concepts provide a mechanism for documenting data flows and tracing changes in data elements either forward from source to destination or backwards from destination to source. Further, presentations of data flows can be defined either at the summary or detail level. At the summary level, presentations of data flows only provide the names and types of systems that data interacts as it flows through an organization. At the detail level, presentations can include specifics about each data point, transport mechanisms, attribute properties, and data quality issues.
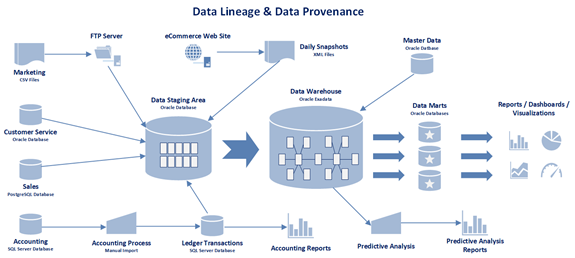
Data Lineage is defined as a life cycle of data elements over time, including the origin of data, what happens to the data, and where the data moves throughout an organization. Data lineage is typically represented graphically to represent data flow from source to destination and how the data gets transformed. A simple representation of data lineage can be shown with dots and lines. The dots represent the data container and the lines represent the movement and transformation of data between the data containers. More complex representations of data lineage contain the type of data container (i.e. application, database, data file, query, or report) and transport method of the data (i.e. FTP, SFTP, HTTPS, ETL, EAI, EII, ODBC, JDBC, etc.)
Data Provenance is a type of data lineage that is specific to database systems and is comprised of the inputs, entities, systems, and processes that untie data within an organization. Moreover, data provenance provides a historical record of data from origin to destination. It is used to trace records through a data flow, to execute a data flow on a subset of inputs, and to debug data flows that contain errors.
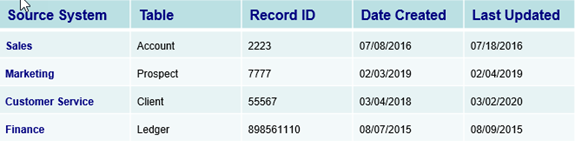
With the use of data provenance, a data scientist or data analyst can ascertain the quality of data within a system, diagnose data anomalies, determine solutions to correct data errors, analyze derivations of data elements, and provide attribution to data sources. Within an organization, data provenance can be used to drill down to the source of data in a data warehouse, track the creation of individual records, and provide a data audit trail of updates of records. Fundamentally, data provenance documents processes that influence data of interest, in effect providing a historical record of the data and its changes over time.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!