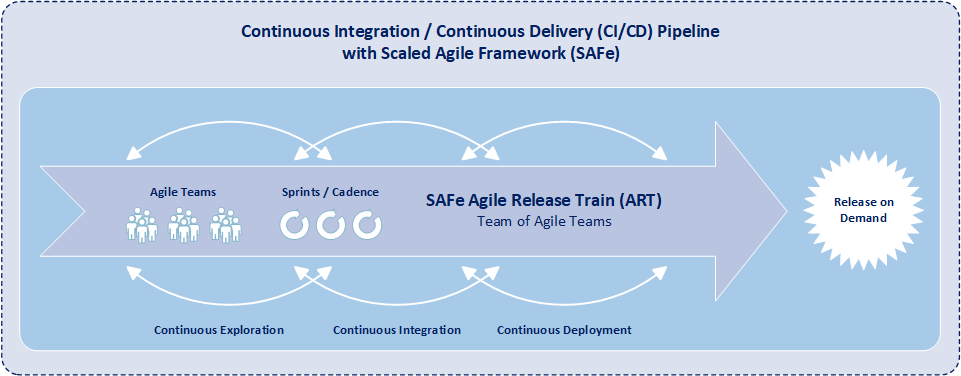
CI/CD Pipeline with Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe)
Continuous Exploration, Continuous Integration, Continuous Deployment, & Release on Demand are the Four Major Aspects of SAFe.
The Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) Pipeline includes the phases, activities, and automation needed to develop and deploy a new software feature or improvement from analysis to an on-demand release to a production environment for use by a system user. The pipeline is a significant element of the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) method for organization-level software development. Moreover, SAFe utilizes a concept known either as agile release train (ART) or solution train (ST). This concept encompasses a team of agile teams collectively responsible for the regular release of features, functionality and improvements. Further, each agile release train independently builds and deploys their own software applications using their own CI/CD pipeline.
The use of a comprehensive CI/CD pipeline provides each agile release train within SAFe with the ability to implement and deploy new or enhanced functionality to users in a more rapid fashion than more conventional software development processes. Conventional practices typically have long implementation cycles, and they tend to deploy large software releases with a great deal of features included. In contrast, the SAFe CI/CD pipeline utilizes short implementation cycles and it enables the deployment of much smaller software releases. Additionally with the SAFe CI/CD pipeline, software modules are developed and deployment of software releases occur as needed. This could be several times a day, several times a week, weekly, or monthly depending on the when the functionality is required to be deployed.
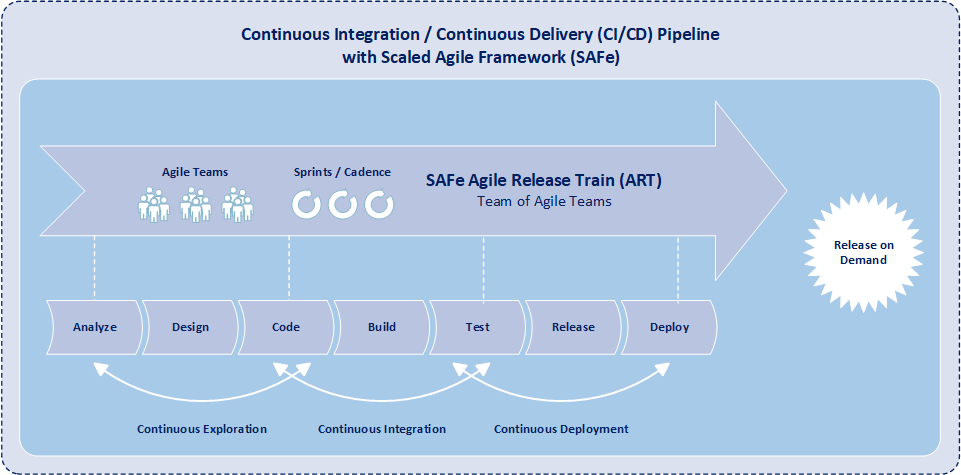
In the previous diagram, the SAFe CI/CD pipeline is shown to be sequential in which the process follows in order of phases (analyze, design, code, build, test, release, deploy). However in reality, the agile release train conducts many of the tasks in parallel. Additionally, analysts, developers, quality assurance personnel, subject matter experts, and operations staff of the agile release train typically all work on tasks at the same time but not necessarily on the same feature. With a shared vision and with team members working concurrently, every agile release train increment and iteration includes: Analysis of requirements, development of functionality, quality assurance, feature demonstrations, deployments to production, and the realization of value.
The SAFe CI/CD Pipeline Includes Four Distinct Aspects:
Continuous Exploration is the process in which user and business needs are identified and features that address those needs are defined. The focus of continuous exploration is to create alignment between what is needed to built and what can be built. During continuous exploration, ideas and concepts are continuously converted into features and specifications of the features are continuously provided. Continuous exploration replaces the conventional waterfall approach of defining all systems requirements at the beginning of the implementation with a more rapid process that generates a consistent flow of features that are ready for the agile release train to implement. Features are defined as small units of work that can travel easily and quickly flow through the remaining aspects of the pipeline. Additionally, within in the continuous exploration process, features are prioritized within the release train backlog.
Continuous Integration is the process of taking features from the release train backlog and building the features into working software modules. Within continuous integration software modules are developed, tested, integrated, and validated in either a pre-production or staging environment where the working software modules are ready for deployment and release. Additionally continuous integration includes a practice in which the merging and testing code of code is automated and code is constantly being integrated into a shared code repository. While automated testing is not required as part of continuous integration, it is typically implied. Continuous integration enables agile release trains to effectively collaborate in the development of different components of a complete software application.
Continuous Deployment is the process of taking completed and validated software modules located in either a pre-production or staging environment and migrating them into a production environment. Once migrated to a production environment, the software modules are verified and monitored to ensure that they are working properly. At this point in the process, software modules become part of the deployed solution and are able to be fully-utilized. This aspect of continuous deployment allows the organization to release, respond, rollback, or fix deployed software modules.
Release on Demand is the ability to make competed software modules and functionality available to system users either all at once or in a incremental/staggered fashion. Subsequently, the business determines the appropriate time to release the completed software modules to groups of system users. New functionality can be released to all system users as soon as it is developed. But more often aspects of each release are provided to groups of system users, timed for when the groups need the new functionality or for when it makes business sense to release new functionality.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!