What is the Common Data Model?
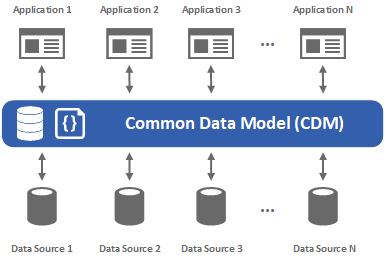
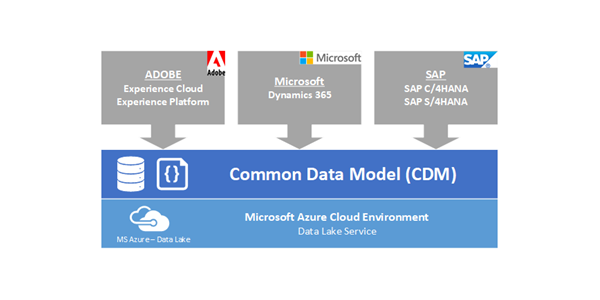
The Common Data Model (CDM) is a standard and extensible collection of data entities, attributes, & relationships that represent business concepts and activities that are common among companies and organizations. Further, CDM is a major component of the Open Data Initiative (ODI), a jointly-developed venture by Microsoft, Adobe, and SAP. It is purposely designed to facilitate data interoperability, information exchange among corporate information systems, rapid application development, and sophisticated data analytics.
Common Data Model Schema
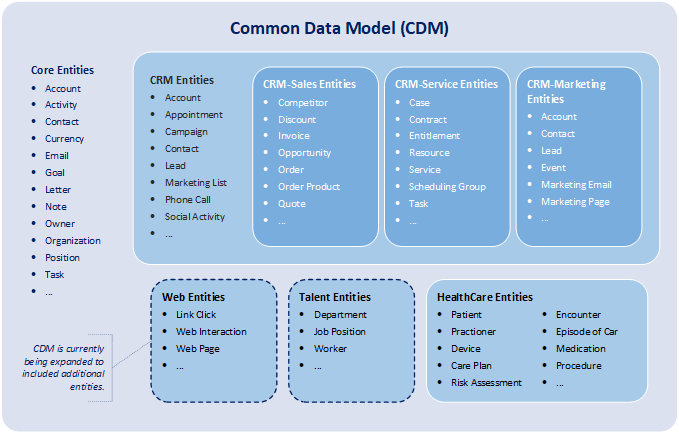
Fundamentally. CDM is a set of shared well-defined data schema that can be used by both transactional and analytical applications. It consists of a set of a standardized, extensible data models published by Microsoft and partners that enable consistency of data and its meaning across applications and business processes. CDM defines a common definition and design for business entities covering the full range of business processes across common business processes including sales, services, marketing, operations, finance, talent, web, healthcare, and commerce. Commonly used data entities included within CDM include: account, case, campaign, opportunity, lead, order, contract, activity, contact, organization, & department, & worker. Fundamentally, data stored within the CDM format provides data schema consistency across applications and system implementations.
Purposes for the Common Data Model
1) Bringing organizational data together within a standardized format.
2) Enablement of rapid development of custom applications.
3) Extending standard entities by either adding to existing entities or creating new entities that are unique to your organization.
4) Integrating data from multiple disparate data sources.
5) Conducting data analysis, business intelligence, and data science.
6) Creating repositories of data within a MS Azure Data Lake.
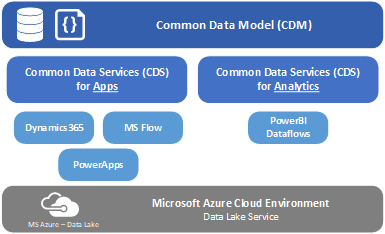
CDM and Common Data Service (CDS)
CDM is currently used within Microsoft’s CDS for Apps and within CDS for Analytics.
CDS for Apps provides the capability to bring data together within the standardized format of the CDM, the capability to store the data within schematized files in an MS Azure Data Lake, and the capability to rapidly develop custom applications and workflows based on that data. The applications and services that can utilize the CDS for Apps are Dynamics 365, MS Flow, and PowerApps.
CDS for Analytics utilizes PowerBI dataflows to enable analysis on data stored within the CDM. Thus providing organizations with a centralized, comprehensive picture of their business to analyze. Like the CDS for Apps, the CDS for Analytics utilizes a MS Azure Data Lake, enables users to query data pulled from multiple sources, and enables Power BI to more easily connect to and share data with third-party applications.
Both the CDS for Apps and CDS for Analytics platforms also offer data integration capabilities through Power Query Online, a data connection technology that provides the ability to discover, connect, combine, and refine data from multiple sources. Power Query Online enables users to import data from a variety of sources, transform it, and then either map the data to standard entities in the CDM or to create custom entities. Power Query Online leverages the same visual, self-service data-prep experience as Power Query within MS Excel and Power BI Desktop.
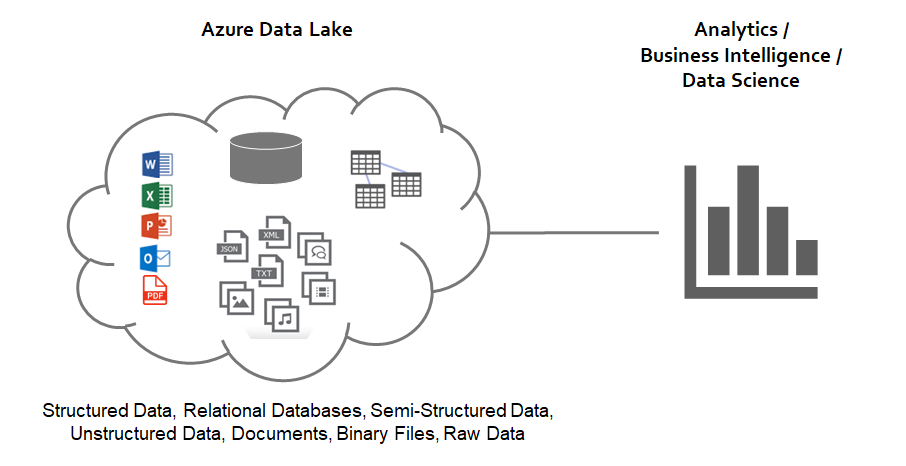
CDM and Data Lakes
CDM uses a common data lake service known as Azure Data Lake Storage (Gen2) on the Microsoft Azure cloud environment as the data repository and foundation of data storage. In general, data lakes include the capabilities to store any type of data and enable both processing and analytics across many platforms and environments. And the common data lake service within MS Azure allows organizations their choice of both development tools and applications to build and deploy applications including MS Dynamics 365, MS Flow, PowerApps, and Power BI. Further, with a single, comprehensive view of data, organizations can discover in real-time more about customers, identify ways to maximize operations, and find ways to provide unique experiences to customers.
Azure Data Lake Storage (Gen2) is designed specifically for organization to execute large-scale analytics, business intelligence, and data science all within the same cloud environment. Moreover, Azure Data Lake is Microsoft’s highly-scalable data repository constructed primarily for big data analytics. Moreover, it has been designed and constructed for the cloud, compatible with HDFS, and can handle massive amounts of data. Additionally, a wide variety of applications, systems, and services can access data from the data lake storage area. And the CDM in the Azure Data Lake provides a mechanism that describes both the standard and extended entities included in the comprehensive data schema. The standardized metadata and self-describing data in the Azure Data Lake Storage helps facilitate data discovery, enables integration between applications, and enables the software tools that can analyze data. Analytic tools that are built into Microsoft Azure cloud environment include: Power BI, Azure Data Factory, Azure Databricks, and Azure Machine Learning Service.