Data Warehouse Concept
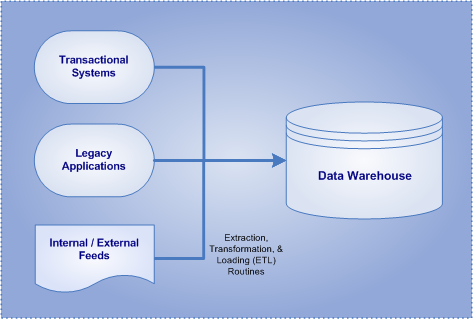
Data Warehouses (DW) are read-only, integrated databases designed to provide insight into past organizational performance and project future results. Further, they can be defined as highly-optimized data repositories that include data sourced from numerous transactional, legacy, external systems, applications, data feeds, and data files that exist throughout an organization.
In practice, the data warehouse is designed, organized, and optimized for retrieval and analysis of data while providing managers, executives, and other decision makers with a single and complete view of the truth. Moreover, the data warehouse is a data repository completely designed for decision-support, analytical-reporting, managing performance, and the conversion of raw data into information. The data warehouse is constructed with a focus on data retrieval and the data warehouse enables complex queries to be performed without any impact on the systems that support the business’ primary transactions (i.e. transactional, operational, and mainframe applications). In contrast to its source databases, the data warehouse is a collection of data designed to support management decision making and contains a wide variety of data that business personnel can use to gain a better understanding of business conditions.
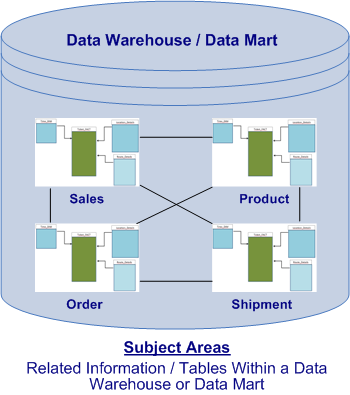
Fundamentally, a data warehouse is unique database in which data is collected for analysis and to support management decision making. A data warehouse is defined by its purpose and it comprises data that is subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant, and non-volatile. This means the data warehouse is focused on a business concept like sales, orders, fulfillments, as opposed to a specific business process.
Read more